Professional performance
with Eye-Tracking
Assess and measure your teams performances
L’eye-tracking è una tecnologia che permette di osservare e comprendere a fondo l’ambiente di lavoro all’interno del quale il tuo team sta operando, osservando i processi da un punto di vista privilegiato: in prima persona.
Osservare in prima persona l’interazione dei membri del team con l’ambiente che li circonda nelle diverse fasi dei processi produttivi permette di evidenziare possible areas of friction, fine tune your improvement interventions and observe the performance of highly qualified professionals, with the aim of illustrating procedures to the training team and reducing risks.
Training
Incorporare l'eye-tracking nei processi formativi permette un feedback in tempi e contesti reali e la possibilità di riguardare le attività post-sessione, riflettendo sull'errore e le aree di miglioramento.
Safety
Highlight potential areas of friction, identify sources of error or confusion that may generate safety issues or risks for your operators.
Produttività e Qualità
Osservare e individuare le migliori pratiche di esecuzione di un compito che, a parità di qualità di risultato, permettono di ottimizzare tempi e costi.
Perché l'eye-tracking?
La tecnica di eye-tracking permette di osservare la distribuzione dell’attenzione di operatori ed operatrici ed il loro comportamento durante l’esecuzione di un compito.
L’eye-tracker è uno strumento tool and molto affidabile che può essere usato insieme ad altri strumenti protettivi senza inficiare il compito o la sicurezza durante l’esecuzione. Allo stesso tempo, permette di registrare dati ottenuti in tempo reale in quelle fasi di esecuzione di un compito in cui le competenze vengono messe in pratica e possono quindi essere misurate oggettivamente.
Perché misurare la professional performance?
Diversi metodi portano, di conseguenza, a diversi risultati: comprendere in che modo il tuo team porta a termine ogni compito può aiutarti ad individuare le best-practice che possono ottimizzare ogni fase del processo, capitalizzando quelle conoscenze che derivano dall’esperienza sul campo, riducendo l’errore ed aumentando la sicurezza.
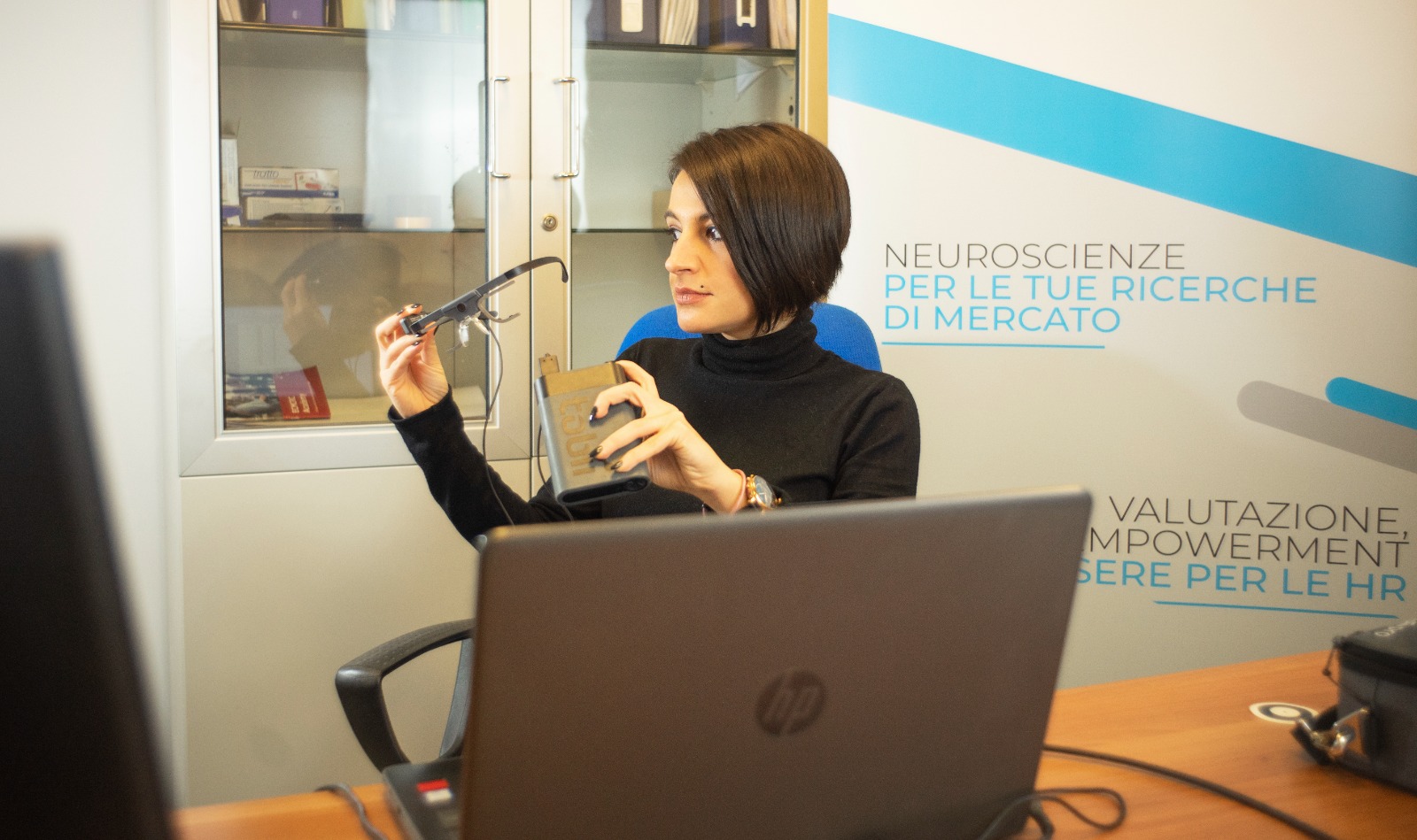

What we measure
L’eye-tracking consente di raccogliere ed analizzare un’ampia gamma di dati che possono essere utilizzati come indicatori di performance.
Classic outputs include heatmaps, delle mappe di calore che indicano le aree di interesse sulle quali sguardo si sofferma più o meno a lungo, senza tuttavia darci maggiori informazioni di temporalità e consequenzialità, ed i gaze plots, ovvero i tracciati di osservazione di un utente che contengono anche informazioni temporali di consequenzialità dei movimenti oculari (saccades) and fixations.
Learn more on our HR Blog
Lots of content from the world of scientific research, edited and reviewed by our team, where we explain the potential of neuromanagement and research techniques from behavioural sciences and neuroscience, applied to the world of HR.